The lotus root is widely used in the cooking of many Asian countries, including China, Japan, and Korea. The lotus plant is well-known in Asia for its tasty root, which is actually the submerged stem of the plant. Lotus root’s crunchiness and mild, somewhat sweet flavour make it an adaptable component.
Lotus root is commonly used as a garnish, in stir-fries, and in pickles in Asian cooking. It’s often deep-fried and served as a snack, and it’s a common component of soups and stews. In traditional Asian medicine, lotus root is valued for its medicinal properties and is used for a variety of purposes, including as a source of vitamins and minerals and to aid in digestion.
As a result of its widespread use in Asian cooking, lotus root can now be found in the produce sections of many supermarkets outside of Asia.
Its Unique Taste and Texture
The flavour and consistency of lotus root are unlike those of any other type of root vegetable. With its mild, somewhat sweet flavour, it can be utilized in a wide range of cuisines. Being crispy and crisp, it is used in both raw and cooked preparations.
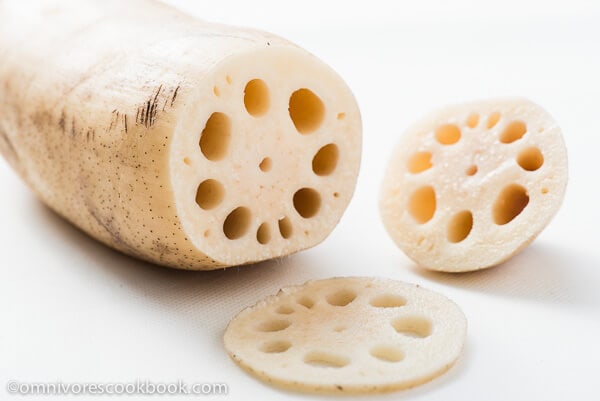

Lotus root has a distinctive texture that makes it a popular addition to dishes like salads, stir-fries, and tempura when a crisp bite is needed. Lotus root, when sliced thin and deep-fried, acquires a delicate, crispy texture that manages to be both crunchy and sensitive. Lotus root is a great vegetable to offer a textural contrast to soups and stews since it stays crunchy even when cooked.
Lotus root’s flavour complements a wide range of foods, from meats and seafood to vegetables. Soy sauce, ginger, and garlic are common Asian seasonings used to complement its mild flavour. As a result of its adaptability and unique flavour and texture, lotus root is becoming increasingly popular as a culinary component in Asia and beyond.
Related: 13 Best High Protein Breakfast Options
Lotus Root Nutrition Facts
Here is a nutritional profile for 100 grams of raw lotus root:
- Calories: 82
- Total Fat: 0.3 g
- Saturated Fat: 0.1 g
- Cholesterol: 0 mg
- Sodium: 3 mg
- Total Carbohydrates: 19 g
- Dietary Fiber: 3 g
- Sugar: 4.2 g
- Protein: 2 g
Nutritional Value of Lotus Root
Many vitamins and minerals may be found in lotus root, making it a healthy addition to any recipe. Lotus root contains a number of important nutrients, including:
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is an antioxidant that serves to boost the immune system and guard against the harm that can be caused to cells. Lotus root is a strong source of vitamin C.
- Potassium: The lotus root is an excellent source of potassium, a vital mineral that plays an important role in maintaining healthy heart function and assisting with the regulation of blood pressure.
- Fiber: The lotus root is an excellent source of the dietary fibre that assists in the maintenance of healthy digestion and maintains normal levels of blood sugar.
- Magnesium: Magnesium is a mineral that is important for many physiological activities, including the regulation of heart rate as well as the function of muscles and nerves. Lotus root is a good source of magnesium, which is a vital mineral.
- Phosphorus: Phosphorus is an essential mineral for maintaining strong bones and teeth as well as a healthy energy metabolism, and lotus root is an excellent supplier of this mineral.
- Folate: The lotus root is an excellent source of folate, which is a B vitamin that plays a critical role in the development and function of cells and is especially crucial for women who are pregnant.
- Iron: The lotus root is an excellent source of iron, a mineral that is necessary for the development of red blood cells and the transportation of oxygen throughout the body.
Its Minimal Calories and How It Help a Healthy Diet
Lotus root has only 82 calories per 100 grams. It’s good for dieters and weight watchers. Lotus root is a low-calorie source of fiber, vitamin C, potassium, and magnesium. Lotus root fiber promotes fullness and satiety, making it a healthy choice for dieters.
Lotus root nutrients also boost health. Lotus root contains potassium, which regulates blood pressure and supports heart health, and vitamin C, which supports the immune system and protects cells. Lotus root magnesium supports muscular and nerve function and heart rate.
Finally, lotus root’s minimal calories and wide spectrum of nutrients make it a healthy choice. It can be eaten as a snack, added to salads, stir-fries, or soups and stews. Lotus root supports a balanced diet and well-being.
Related: 10 Most Important Times During the Day to Drink Water
Health Benefits of Lotus Root
Benefits for Digestion and Heart Health

The lotus root is a nutrient-dense ingredient that may have a number of positive effects on your health, particularly with regard to digestion and the cardiovascular system. Consuming lotus root is associated with numerous positive health effects, including the following:
Improved Digestion
The lotus root is an excellent source of the dietary fiber that can assist in the maintenance of healthy digestion as well as regularity. The fiber in lotus root can also assist to manage blood sugar levels and encourage sensations of fullness and satiety, both of which are supported by the root’s high fiber content.
Heart health
The lotus root is an excellent source of the mineral potassium, which plays a key role in the maintenance of healthy cardiac function and in the control of blood pressure. Additionally, the fiber included in lotus root can assist in lowering cholesterol levels, which in turn reduces the chance of developing cardiovascular disease.
Immune support
Vitamin C is an antioxidant that serves to boost the immune system and guard against the harm that can be caused to cells. Lotus root is a strong source of vitamin C.
This Have Anti-inflammatory Properties
Inflammation can be reduced and general health can be improved thanks to the presence of anti-inflammatory chemicals in lotus root, which have the potential to do just that.
Improve Bone Health
Phosphorus is an essential mineral for maintaining strong bones and teeth as well as a healthy energy metabolism, and lotus root is an excellent supplier of this mineral.
Lotus Root Help to Decrease Blood Sugar Levels
Lotus root is high in fiber, with 3 grammes per 100 grammes. Lotus root fiber regulates blood sugar in numerous ways. Fiber slows carbohydrate digestion, avoiding blood sugar increases. This can assist diabetics stabilize their blood sugar.
Fiber also promotes fullness and satiety, which lowers blood sugar. This reduces carbohydrate intake, regulating blood sugar. Finally, fiber improves insulin sensitivity, which helps regulate blood sugar levels. This can assist blood sugar management in diabetics.
In conclusion, lotus root fiber helps maintain blood sugar levels and prevent fast spikes. Lotus root provides minerals that assist overall health, including stable blood sugar levels.
Culinary Uses of Lotus Root
The Various Ways Lotus Root Can Be Prepared
The lotus root is a multifunctional component that can be prepared in a wide range of different ways. The following are some of the most common culinary applications of lotus root:
- A snack with a texture similar to that of nuts can be made by slicing lotus root into rounds and then frying it until it becomes crisp.
- The lotus root can also be sliced and stir-fried with other ingredients to create a dish that is both savoury and nutritious. These other items can include vegetables or meats.
- After being boiled or steamed until it is tender, lotus root can be prepared as a side dish, added to soups or stews, or used in other culinary applications.
- Pickled lotus root can be used as a condiment or as a snack, lending meals a sour flavour and a crisp bite to the food it complements.
- You may grate lotus root and use it as a topping for foods like salads or rice bowls. You can also eat the root alone.
- A dish that is both sweet and savoury can be made by baking or roasting lotus root in the oven until it is soft and has a caramelised texture.
- You can also puree lotus root and use it as a thickening for sauces or soups, or as a basis for sweets like puddings or custards. These uses require that the lotus root be cooked first.
Dishes that Feature Lotus Root
The lotus root is a versatile component that is utilised in a wide variety of recipes across a number of different Asian cuisines. The following is a list of well-known meals that feature lotus root:
- Kinpira gobō: A food that is considered to be of Japanese origin and is prepared by stir-frying sliced lotus root with soy sauce, sugar, and ginger.
- Lotus root soup: A hearty and satisfying soup that is prepared by slowly cooking sliced lotus root in a broth, typically together with other vegetables like mushrooms, carrots, and ginger.
- Lotus root stir-fry: A delicious stir-fry dish that is prepared with sliced lotus root, a variety of veggies, and a savoury sauce.
- Lotus root tempura: Slices of lotus root are dipped in a batter and then deep-fried until they are brown and crispy.
- Braised lotus root: Slices of lotus root braised in a fragrant sauce over a low heat until soft and infused with the taste of the sauce.
- Lotus root salad: A revitalizing salad that is prepared by combining shredded lotus root with dressing and many additional components, such as greens and vegetables.
- Stuffed lotus root: The lotus root is baked or steamed after being packed with a variety of items including pork, veggies, or rice.
Frequently Ask Questions
- Food Literacy Center. Lotus root.
- USDA FoodData Central. Lotus root, cooked, boiled, drained, without salt.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. Potassium: Fact sheet for health professionals.
- American Heart Association. How to eat more fruits and vegetables.
- University of California San Francisco Health. Constipation.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. Folate: Fact sheet for health professionals.